- Whirlwind, Lists, Loops, Cond. Stmts., Functions, Modules, Dicts
- What is the difference between a list and a dictionary?
- How do you write a module in Python?
- Files, CLI, OO, Exceptions
- How do you open a file in Python?
- How do you throw an exception in Python?
- Intro to Plotting
- How do you plot a line chart in Matplotlib?
- What is an axis in a Matplotlib plot?
- Intro to Numpy and Plotting Cntd.,
- What does it mean that an array has a shape?
- How do you plot multiple lines in Matplotlib?
- Intro to Pandas
- What is a
DataFrame? - How do you access a row in a
DataFrame?
- What is a
- Multiprocessing, generators and intro to Requests
- What is the difference between an iterator and a generator?
- How do you parallelise programs in Python?
- Graphs & PageRank
- What is a graph?
- Why does the PageRank algorithm exist?
- Webscraping Basics, Regular Expr. & Selenium
- What is a regular expression?
- What is Selenium?
- Feature spaces
- What is a feature?
- What is a feature vector?
- Neural Networks
- What is a neuron?
- What is an activation function?
- Image Proc. (OpenCV)
- How do you represent an image in a Numpy array?
- What is a colour space?
- Movement Detection
- What is an ‘object’?
- How does movement detection work?
Whirlwind, Lists, Loops, Cond. Stmts., Functions, Modules, Dicts
What is the difference between a list and a dictionary?
A list is an ordered sequence of elements. The elements can have any type, and the elements don’t have to be of the same type.
A dictionary is an unordered set of key-value pairs. The keys can have any hashable type, while the values don’t have any type restrictions.
The elements of a list can be accessed by their index, whereas the values of a dictionary is accessed by their key.
How do you write a module in Python?
Python modules are .py files that consist of Python code. Any Python file can be referenced as a module.
Some modules are available through the Python Standard Library, while others can be installed with Python’s package manager pip.
You can write your own module by creating a .py file. In this file you can write Python code like you would do in any Python script. To use this module in another Python script, you simply just import it and you will be able to use the variables, funtions, and classes you have made in the module with the . notation.
# hello.py
# Define a function
def world():
print("Hello, World!")
# Define a variable
shark = "Sammy"
# Define a class
class Octopus:
def __init__(self, name, color):
self.color = color
self.name = name
def tell_me_about_the_octopus(self):
print("This octopus is " + self.color + ".")
print(self.name + " is the octopus's name.")
# main_program.py
# Import hello module
import hello
# Call function
hello.world()
# Print variable
print(hello.shark)
# Call class
jesse = hello.Octopus("Jesse", "orange")
jesse.tell_me_about_the_octopus()
If you modue contains code that should only run when it is run as the main, you should encapsulate it:
if __name__ == '__main__':
#run code
If not it will run the code when imported.
Files, CLI, OO, Exceptions
How do you open a file in Python?
with open(filename,'w') as file:
#do stuff with file
with makes sure the file gets closed when the script is done with the file. You can open the file without with, the you have to make sure to call .close() on the file.
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| ‘r’ | This is the default mode. It Opens file for reading. |
| ‘w’ | This Mode Opens file for writing. If file does not exist, it creates a new file. If file exists it truncates the file. |
| ‘x’ | Creates a new file. If file already exists, the operation fails. |
| ‘a’ | Open file in append mode. If file does not exist, it creates a new file. |
| ‘t’ | This is the default mode. It opens in text mode. |
| ‘b’ | This opens in binary mode. |
| ’+’ | This will open a file for reading and writing (updating) |
How do you throw an exception in Python?
x = 10
if x > 5:
raise Exception('x should not exceed 5. The value of x was: {}'.format(x))
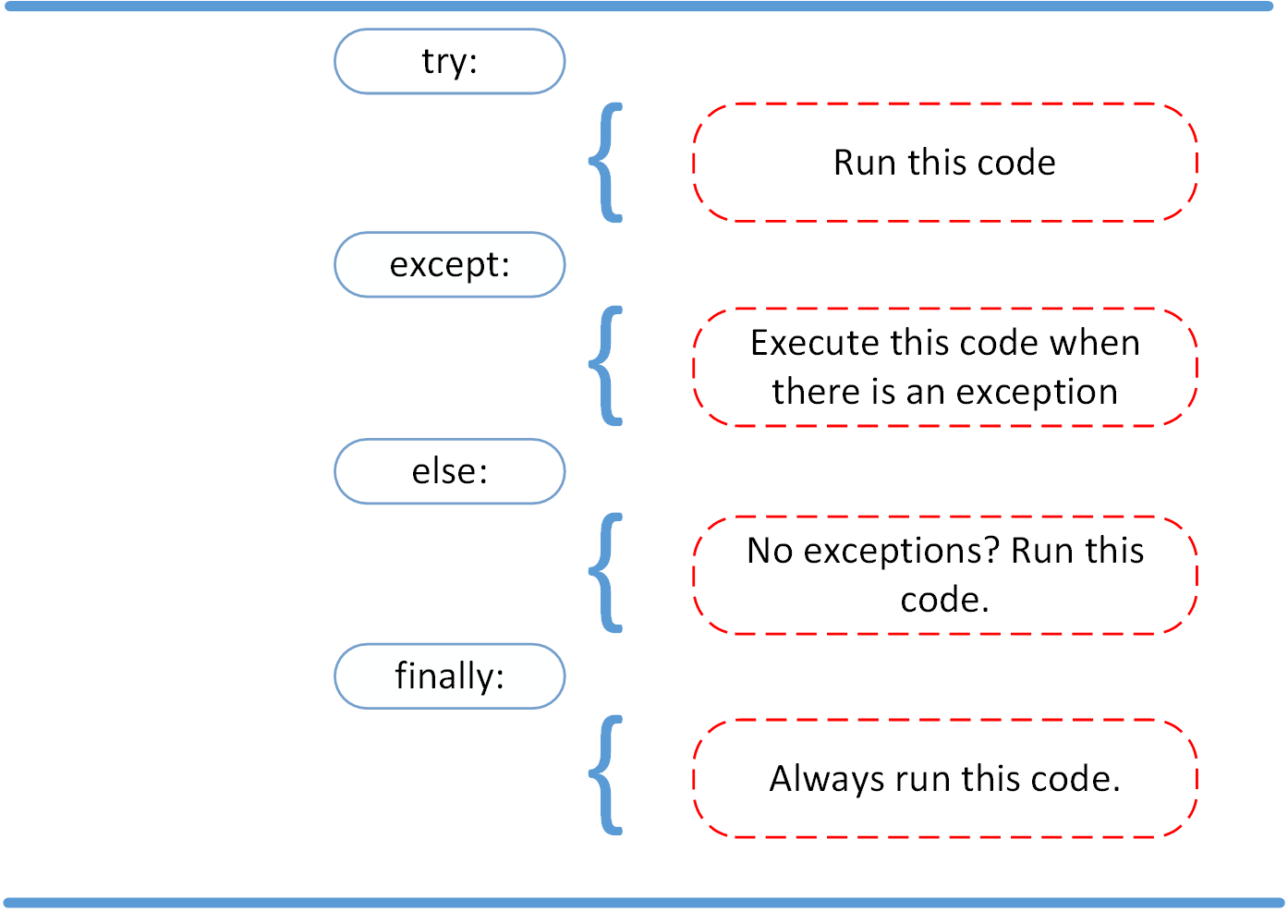
def linux_interaction():
assert ('linux' in sys.platform), "Function can only run on Linux systems."
print('Doing something.')
try:
linux_interaction()
except AssertionError as error:
print(error)
else:
try:
with open('file.log') as file:
read_data = file.read()
except FileNotFoundError as fnf_error:
print(fnf_error)
finally:
print('Cleaning up, irrespective of any exceptions.')
Intro to Plotting
How do you plot a line chart in Matplotlib?
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot([1,2,3,4])
plt.ylabel('some numbers')
plt.show()

What is an axis in a Matplotlib plot?
matplotlib.axis documentation
Intro to Numpy and Plotting Cntd.,
What does it mean that an array has a shape?
An array has a shape, this is the dimensions of the array eg.
[1,2,3]
has shape (3,) and
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]
]
has shape (2,3) and
[
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]
],
[
[7,8,9],
[10,11,12]
]
]
has shape (2,2,3).
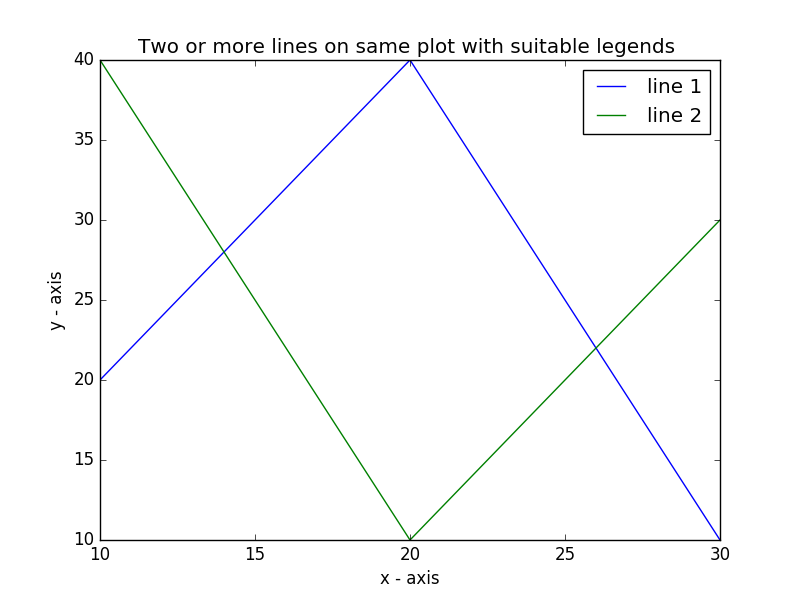
How do you plot multiple lines in Matplotlib?
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# line 1 points
x1 = [10,20,30]
y1 = [20,40,10]
# plotting the line 1 points
plt.plot(x1, y1, label = "line 1")
# line 2 points
x2 = [10,20,30]
y2 = [40,10,30]
# plotting the line 2 points
plt.plot(x2, y2, label = "line 2")
plt.xlabel('x - axis')
# Set the y axis label of the current axis.
plt.ylabel('y - axis')
# Set a title of the current axes.
plt.title('Two or more lines on same plot with suitable legends ')
# show a legend on the plot
plt.legend()
# Display a figure.
plt.show()
Intro to Pandas
What is a DataFrame?
How do you access a row in a DataFrame?
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.read_csv("https://pythonhow.com/data/income_data.csv")
df2 = df1.set_index("State", drop = False)
# Extracting a subset of a pandas dataframe
df2.loc["Alaska":"Arkansas","2005":"2007"]
# Extracting a column of a pandas dataframe
df2.loc[: , "2005"]
df2["2005"]
# Extracting a row of a pandas dataframe
df2.loc["California", : ]
# Extracting specific columns of a pandas dataframe
df2[["2005", "2008", "2009"]]
# Extracting specific rows of a pandas dataframe
df2[1:3]
# Extracting a single cell from a pandas dataframe
df2.loc["California","2013"]
# Position based indexing
df2.iloc[0:3,0:4]
df2.ix[0:3,"2005":"2007"]
Multiprocessing, generators and intro to Requests
What is the difference between an iterator and a generator?

An iterable is an object that implements the __iter__ method. An iterable is any object that can be a file pointer and return an iterator. A Python list object is iterable.
An iterator is an object that implements the iterable protocol as it also responds to the next() method. To use iterable and iterator, there is a simple iterable protocol which is driven by two functions, iter() and next().
A generator is a special kind of iterator. All generators are iterators but all iterators are not generators. Each time the yield statement is executed, the generator function generates a new value.
When a generator function gets called, then a generator object is returned without even beginning the execution of the generator function. When the next() function is called for the first time, the generator function starts executing until it reaches the yield statement. The yielded value is returned by the next() call.
The generator function is that in which the keyword yield appears in its body. The other type of generator is the generator expression, which is equivalent to a list comprehension.
How do you parallelise programs in Python?
Parallel Processing in Python.
Graphs & PageRank
What is a graph?
Python - Graphs
Why does the PageRank algorithm exist?

The formula explained:
The PageRank of a page in this iteration equals 1 minus a damping factor, plus, for every link into the page (except for links to itself), add the page rank of that page divided by the number of outbound links on the page and reduced by the damping factor.